Albis Plastic 開發用于燃料電池應用的化合物
這些化合物目前正在與多家原始設備制造商合作進行驗證。
克萊爾·戈德斯伯里|?2019 年 12 月 3 日
Albis Plastic(德國漢堡)宣布開發用于燃料電池應用的塑料解決方案,目前正在與知名 OEM 的項目中進行驗證。驗證過程包括 Albis 的技術化合物 Altech、Alfater SL TPV、Tedur L PPS 和 Alcom,所有這些都可以適應客戶的特定要求。
電池動力汽車目前正在大規模推向市場,如大眾 ID、奧迪 e-tron、寶馬 i3、歐寶 Ampera-e 和梅賽德斯 EQC 車型。Albis 表示,毫無疑問,駕駛這些車輛時可以減少 CO?2排放,前提是能源來自可再生能源。
然而,該技術帶來了許多需要解決的挑戰,該公司補充說,包括資源的采購、每次裝載的最大范圍以及相關的裝載時間。
|
|
|
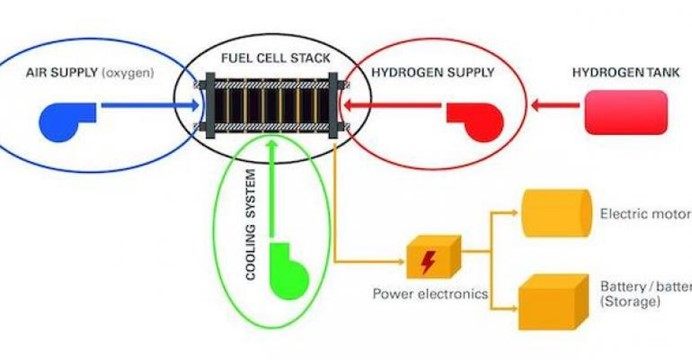
燃料電池系統需要在燃料電池核心本身以及氫氣、氧氣、空氣供應和冷卻回路中使用多種材料,包括金屬、塑料和密封材料。?圖片由 Albis Plastic 提供。 |
"結合電池和燃料電池的混合解決方案在這里是一個很有前途的解決方案,"Albis 管理委員會成員兼復合業務負責人 Ian Mills 說。
燃料電池系統需要使用多種材料,包括金屬、塑料和密封材料。它們既用于燃料電池核心本身,即所謂的"堆",也用于氫氣、氧氣、空氣供應和冷卻回路。它們還用于泵、閥門、壓縮機、管道和連接器等部件。
諸如揮發性成分或離子之類的污染物會通過排放導致燃料電池的退化,從而通過改變"雙極板"的表面等方式降低其使用壽命和性能。這些揮發性成分可以從燃料電池的各個組件中使用的材料中遷移出來。
"由于有大量單獨的零件和附件,幾乎不可能用完全零排放的組件生產燃料電池系統,"汽車業務開發經理 Thies Wrobel 解釋說。"因此,必須仔細檢查所用材料的排放量。"
另一個重要因素是在清潔的生產環境中使用相同的原材料以一致、可重復的工藝生產材料。考慮到這些因素并與 OEM 合作,Albis 開發了已在冷卻和供氣系統中進行測試的材料。
這些材料包括來自 Altech PP 產品組合的聚丙烯化合物,其中含有 20%、40% 和 50% 的玻璃纖維;Tedur L 產品組合中的 PPS 化合物,含有 30% 和 40% 的玻璃纖維以及 15% 的 PTE(用于軸承應用);和 Alfater TPV,一種過氧化交聯的熱塑性硫化橡膠,具有與彈性體/橡膠相媲美的肖氏 A 60 和 70 硬度(用于密封應用)。
未來,Albis 實驗室將在專門安裝的測試臺上測試其他化合物。
Albis Plastic develops compounds for fuel-cell applications
The compounds are currently being validated in collaboration with several OEMs.
Clare Goldsberry?| Dec 03, 2019
Albis Plastic (Hamburg, Germany) announced the development of a plastic solution for fuel-cell applications, which is currently being validated in projects with well-known OEMs. The validation process includes Albis' technical compounds Altech, Alfater SL TPV, Tedur L PPS and Alcom, all of which can be adapted to customer-specific requirements.
Battery-powered cars are currently being introduced to the market on a large scale, such as the VW ID, Audi e-tron, BMW i3, Opel Ampera-e and Mercedes EQC models. Albis stated that it has no doubt that CO2?emissions can be reduced while driving these vehicles, provided the energy comes from renewable sources.
However, this technology poses a number of challenges that need to be addressed, added the company, including the procurement of resources, the maximum range per load and the associated duration of loading times.
|
|
|
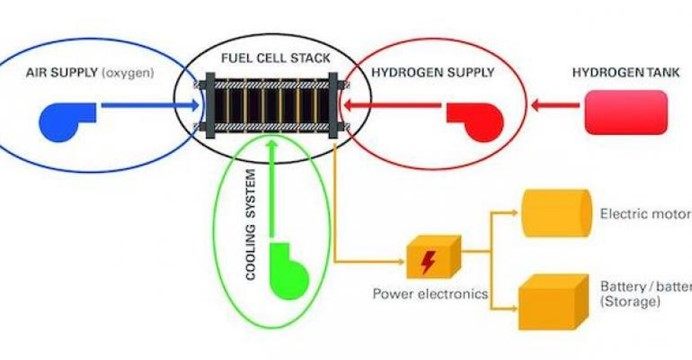
Fuel-cell systems require the use of numerous materials, including metals, plastics and sealing materials, in the fuel-cell core itself as well as the hydrogen, oxygen, air supply and cooling circuit.?Image courtesy Albis Plastic. |
"Hybrid solutions that combine battery and fuel cells are a promising solution here," said Ian Mills, a member of the Albis Management?Board and head of the Compounding business.
Fuel-cell systems require the use of numerous materials, including metals, plastics and sealing materials. These are used both for the fuel cell core itself, the so-called "stack," and the hydrogen, oxygen, air supply and cooling circuit. They are also used in components such as pumps, valves, compressors, pipes and connectors.
Pollutants, such as volatile components or ions, can contribute to the degradation of the fuel cell through emissions and, thus, reduce its service life and performance by changing the surfaces of the "bipolar plates," for example. These volatile components can migrate from the materials used in the individual assemblies of the fuel cell.
"The production of a fuel-cell system from completely emission-free components is almost impossible because of the large number of individual parts and attachments," explained Thies Wrobel, Business Development Manager—Automotive. "Therefore, the materials used must be carefully examined for emissions."
Another important factor is production of the materials in a consistent, reproducible process using the same raw materials in a clean production environment. Given these considerations and in cooperation with OEMs, Albis has developed materials that have been tested in cooling and air supply systems.
The materials include polypropylene compounds from the Altech PP portfolio with 20%, 40% and 50% glass fibers; PPS compounds from the Tedur L portfolio with 30% and 40% glass fibers plus 15% PTE (for bearing applications); and Alfater TPV, a peroxidically cross-linked thermoplastic vulcanizate with comparable properties to elastomer/rubber in Shore A 60 and 70 hardness (for sealing applications).
Additional compounds will be tested in the future at Albis' laboratory on a specially installed test rig.
 艾邦氫能產業鏈通訊錄,目前有2200人加入,如億華通、清極能源、氫藍時代、雄韜、氫牛、氫璞、愛德曼、氫晨、喜馬拉雅、明天氫能、康明斯、新源動力、巴拉德、現代汽車、神力科技、中船712等等,可以按照標簽篩選,請點擊下方關鍵詞試試
資料下載:
艾邦氫能產業鏈通訊錄,目前有2200人加入,如億華通、清極能源、氫藍時代、雄韜、氫牛、氫璞、愛德曼、氫晨、喜馬拉雅、明天氫能、康明斯、新源動力、巴拉德、現代汽車、神力科技、中船712等等,可以按照標簽篩選,請點擊下方關鍵詞試試
資料下載:



